1. Why ACH Matters
Ever wondered why your cleanroom’s energy bills are through the roof even though it passes ISO 14644 particle tests?
The hidden culprit is often a misunderstood metric: Air Changes per Hour (ACH).
ACH isn’t just about moving air—it’s about ensuring contamination control, regulatory compliance, and energy efficiency. Get it wrong, and you risk sterility failures or astronomical operating costs.
2. The Problem With Rules of Thumb
For decades, engineers relied on “rules of thumb” like:
- ISO Class 5 (Class 100): ~240–360 ACH
- ISO Class 7 (Class 10,000): ~60–90 ACH
- ISO Class 8 (Class 100,000): ~20–30 ACH
These values are approximate, based on older standards and turbulent airflow cleanrooms. Modern guidelines (EU GMP Annex 1, ISPE) emphasize that airflow type, occupancy, and activity levels matter more than fixed numbers.
- Overdesign = skyrocketing energy costs.
- Under design = compliance and product failure risks.
⚡ Enjoying this article? Stay updated with weekly HVAC & Energy Hacks — straight on WhatsApp!
💚 Join Our WhatsApp Channel3. How ACH Should Be Calculated
The real formula is simple but often misapplied:
ACH = (Supply airflow × 60) ÷ Room volume
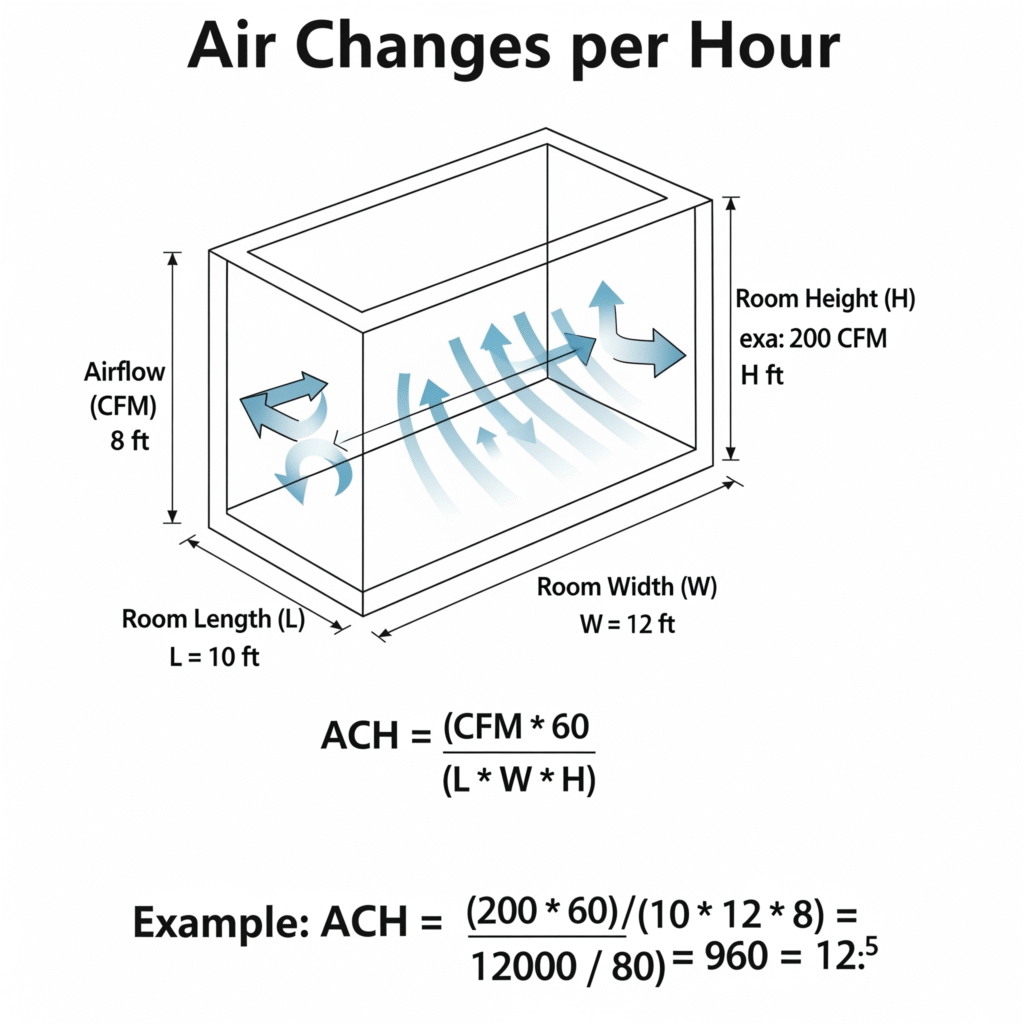
- If using metric units:
- Supply airflow in cubic meters per hour (m³/h)
- Room volume in cubic meters (m³)
- If using imperial units:
- Supply airflow in cubic feet per minute (CFM)
- Room volume in cubic feet (ft³)
💡 Pro Tip: Use one unit system consistently to avoid confusion.
For complex geometries or high-risk areas, engineers often validate with CFD simulations and particle counts rather than relying on paper calculations alone.
4. Where Engineers Go Wrong
- Copy-paste design values: A value that worked in one project may be overkill in another.
- Ignoring pressure cascades: High ACH is useless if airflow direction is wrong.
- Validation surprises: In one pharma audit, a facility designed for ISO 7 failed particle tests because operators overloaded the space—ACH was correct, but occupancy wasn’t factored in.
📌 Energy Hook: According to U.S. DOE and ASHRAE data, overventilation can waste 40–60% more energy in HVAC systems. That’s money literally being blown away.
5. The Smarter Way: Data + Tools
Instead of guesswork, modern engineers use calculation tools that:
- Factor in HEPA efficiency, occupancy, and risk class
- Simulate different scenarios (ISO 5 vs ISO 7)
- Recommend optimized ACH instead of blindly following rules
👉 Try our Utility Performance Tool. It’s free to use and gives instant results—helping you design systems that are both compliant and energy efficient.
6. Final Word
Air changes per hour might look like a simple number, but it’s the backbone of cleanroom HVAC design.
Get it wrong, and you bleed money or fail compliance.
Get it right, and you strike the balance between sterility assurance and sustainability.
🚀 In our next post, we’ll dive into Pressure Cascades: The Invisible Shield That Keeps Cleanrooms Sterile.


Really insightful to learn about ACH.
Thank you Mr. Aslam
Good one.
Good Read